Spring Security 를 실습하고 기록해보자.
Spring Security 란?
Spring 에서 제공해주는 보안 솔루션이다. 개발자가 직접 보완 관련 코드를 짤 필요없기 때문에 매우 간편하다. Spring Security 에서는 인증(Authentication) 과 권한(Authorization) 기능을 모두 제공하고 있어, 이 개념을 알아야 한다.
인증과 권한
인증(Authentication) 과 권한(Authorization) 을 살펴보면, 인증은 '나'='나' 라는 것을 확인하는 절차이고, 권한은 '나' 는 어느범위까지 사용이 가능한 지를 결정하는 것이다.
Spring Security 를 사용하는 이유
- Require authentication to every URL in your application
- Generate a login form for you
- Allow the user with the Username user and the Password password to authenticate with form based authentication
- Allow the user to logout
- CSRF attack prevention
- Session Fixation protection
- Security Header integration
- HTTP Strict Transport Security for secure requests
- X-Content-Type-Options integration
- Cache Control (can be overridden later by your application to allow caching of your static resources)
- X-XSS-Protection integration
- X-Frame-Options integration to help prevent Clickjacking
- Integrate with the following Servlet API methods
예제
예제 설명
Spring Security 를 이용하여 간단한 회원가입 / 로그인 기능 구현해보도록 하자. 이 과정에서 Spring Data JPA 도 사용되는데 이 주제는 다음에 다뤄보도록 하자.
총 4개의 화면으로 구성된다. + H2 Console 화면 (실제 사용자 정보가 저장되는 지 확인해보자)
- 로그인 화면
- 회원가입 화면
- 사용자 화면
- Admin 화면
총 6개의 package 로 소스코드를 관리한다.
- config
- domain
- repository
- dto
- service
- controller
시작
1. Spring project 를 하나 생성하자.
- Gradle
- Spring Boot 2.6.6
- Java 8
- Jar
2. 의존성 추가
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.thymeleaf.extras:thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
}3. domain - Entity 정보 생성
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@Entity
@Getter
public class UserInfo implements UserDetails {
@Id
@Column(name = "code")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long code;
@Column(name = "email", unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(name = "password")
private String password;
@Column(name = "auth")
private String auth;
@Builder
public UserInfo(String email, String password, String auth) {
this.email = email;
this.password = password;
this.auth = auth;
}
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
Set<GrantedAuthority> roles = new HashSet<>();
for(String role : auth.split("," )) {
roles.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role));
}
return roles;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return password;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return email;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
}회원가입 시 [이메일, 패스워드, 권한] 이 저장될 것이다. 여러개의 권한을 가질 수 있고, 콤마[,]로 구분되어 저장된다. 로그인이 될 때 권한 리스트를 불러와 Spring Security 가 인식할 것이다.
한가지 주목해야 할 점은 UserDetails 라는 인터페이스를 상속받는 것이다. 이것은 Spring 제공 하는 것으로 인증과 권한을 담당한다.
4. repository 생성
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<UserInfo, Long> {
Optional<UserInfo> findByEmail(String email);
}Repository 는 interface 로 생성하고 JpaRepository 를 상속 받는다.
5. dto 생성
@Getter
@Setter
public class UserInfoDto {
private String email;
private String password;
private String auth;
}
6. service 생성
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class UserService implements UserDetailsService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
public Long save(UserInfoDto userInfoDto) {
BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
userInfoDto.setPassword(encoder.encode(userInfoDto.getPassword()));
return userRepository.save(UserInfo.builder()
.email(userInfoDto.getEmail())
.password(userInfoDto.getPassword())
.auth(userInfoDto.getAuth()).build()
).getCode();
}
@Override
public UserInfo loadUserByUsername(String email) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
return userRepository.findByEmail(email)
.orElseThrow(() -> new UsernameNotFoundException(email));
}
}UserDetailsService 를 상속받고 loadUserByUsername 오버라이드 함수를 사용한다.
7. config 생성
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
private final UserService userService;
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/css/**", "/js/**", "/img/**");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login", "/signup", "/user").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/h2-console/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/").hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/admin").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.csrf()
.ignoringAntMatchers("/h2-console/**")
.and()
.headers()
.frameOptions().sameOrigin()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/")
.and()
.logout()
.logoutSuccessUrl("/")
.invalidateHttpSession(true);
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userService).passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
}
}WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 를 상속 받는다. 세 개의 configure 메서드는 역할이 각각 다르다.
configure(WebSecurity web)
// -> static 하위 resource 디렉토리를 접근 불가한 리스트에서 제외할 수 있다.
configure(HttpSecurity http)
// -> http 관련 인증 설정을 담당한다.
antMatchers // 경로 권한 설정을 담당한다.
permitAll // 누구나 접근 가능
hasRole // 기재된 권한이 있는 경우 접근 가능
anyRequest // antMatchers 외 경로
authenticated // 권한 있으면 접근 가능
formLogin() // 로그인 설정
loginPage("/login") // 로그인 화면
defaultSuccessUrl("/") // 로그인 성공 시 이동할 화면
logout() // 로그아웃 설정
logoutSuccessUrl("/") // 로그아웃 시 이동할 화면
invalidateHttpSession(true); // 로그아웃 시 세션 제거 여부
configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)
// -> 로그인 인증을 담당하고, 사용자 정보를 불러온다.8. controller 생성
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Controller
public class UserController {
private final UserService userService;
@PostMapping("/user")
public String signup(UserInfoDto userInfoDto) {
userService.save(userInfoDto);
return "/login";
}
@GetMapping("/logout")
public String logoutPage(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
new SecurityContextLogoutHandler().logout(request, response, SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication());
return "/login";
}
}GET 메소드로도 로그아웃이 가능하다. SecurityContextLogoutHandler 을 사용하면 된다.
이제 View 화면을 구성해보자.
- login.html
- signup.html
- main.html
- admin.html
Controller에 등록을 해도 되지만, WebMvcConfigurer 을 사용하여 이동할 화면을 매핑을 해보자.
9. MVC config 생성
@Configuration
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("main");
registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/admin").setViewName("admin");
registry.addViewController("/signup").setViewName("signup");
}
}
10. View 생성
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Login</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Login</h1> <hr>
<img src="/img/info.jpeg" />
<form action="/login" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" th:name="${_csrf.parameterName}" th:value="${_csrf.token}" />
email : <input type="text" name="username"> <br>
password : <input type="password" name="password"> <br>
<button type="submit">Login</button>
</form> <br>
<a href="/signup">Go to join! →</a>
</body>
</html>
signup.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>sign up</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Sign Up</h1> <hr>
<form th:action="@{/user}" method="POST">
email : <input type="text" name="email"> <br>
password : <input type="password" name="password"> <br>
<input type="radio" name="auth" value="ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_USER"> admin
<input type="radio" name="auth" value="ROLE_USER" checked="checked"> user <br>
<button type="submit">Join</button>
</form> <br>
<a href="/login">Go to login →</a>
</body>
</html>
main.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Main</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>회원 전용 페이지</h2>
ID : <span sec:authentication="name"></span><br>
소유 권한 : <span sec:authentication="authorities"></span><br>
<form id="logout" action="/logout" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" th:name="${_csrf.parameterName}" th:value="${_csrf.token}" />
<input type="submit" value="로그아웃"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
admin.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>관리자 전용 페이지</h2>
ID : <span sec:authentication="name"></span> <br>
소유 권한 : <span sec:authentication="authorities"></span> <br>
<form id="logout" action="/logout" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" th:name="${_csrf.parameterName}" th:value="${_csrf.token}" />
<input type="submit" value="로그아웃"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
11. Spring boot 실행
localhost:8080/ 접속하면 main.html 로 이동이 될 것이다. 근데 로그인 정보가 없으니 /login 화면으로 이동 됨.

사용자 정보가 없기 때문에 signup 을 해보자.
localhost:8080/signup

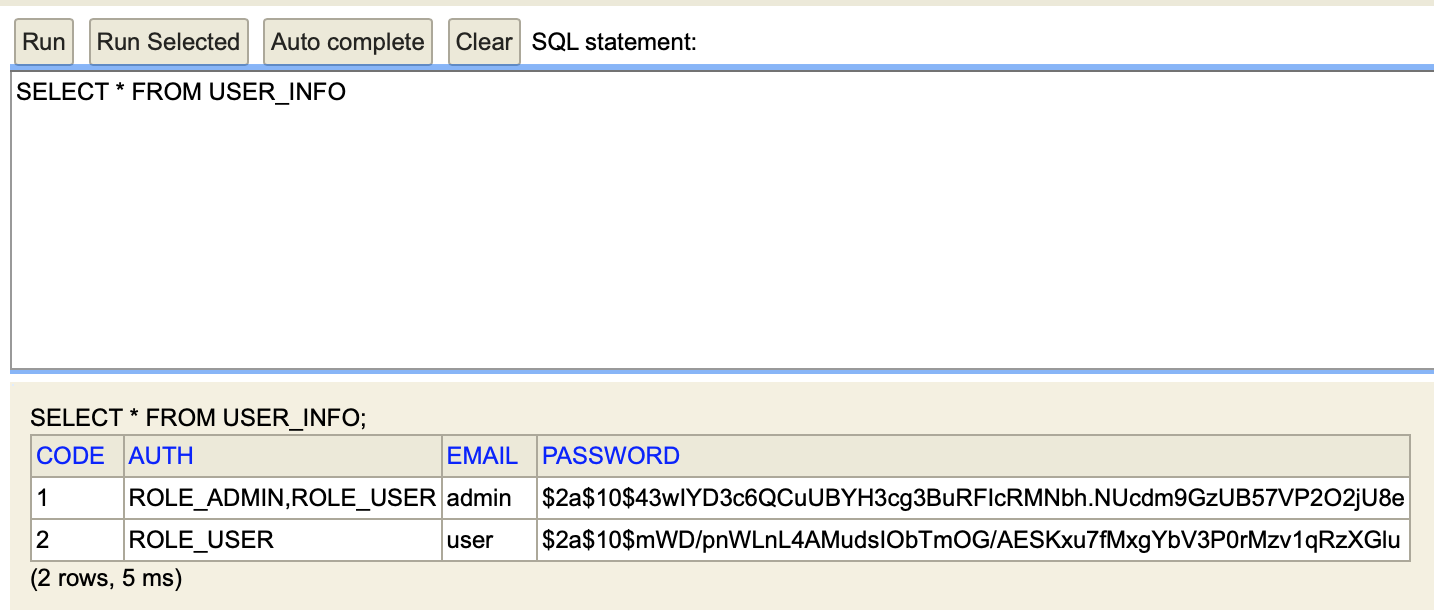
admin 을 선택하는 경우 DB 에 ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN 두개가 들어간다.
H2 console 에서 조회해보면 아래와 같이 조회된다.

이제 로그인을 해보자.
ADMIN, USER 두 권한이 모두 존재하기 때문에, 회원용, admin용 화면 두 곳 모두 접속이 가능한 것을 볼 수있다.

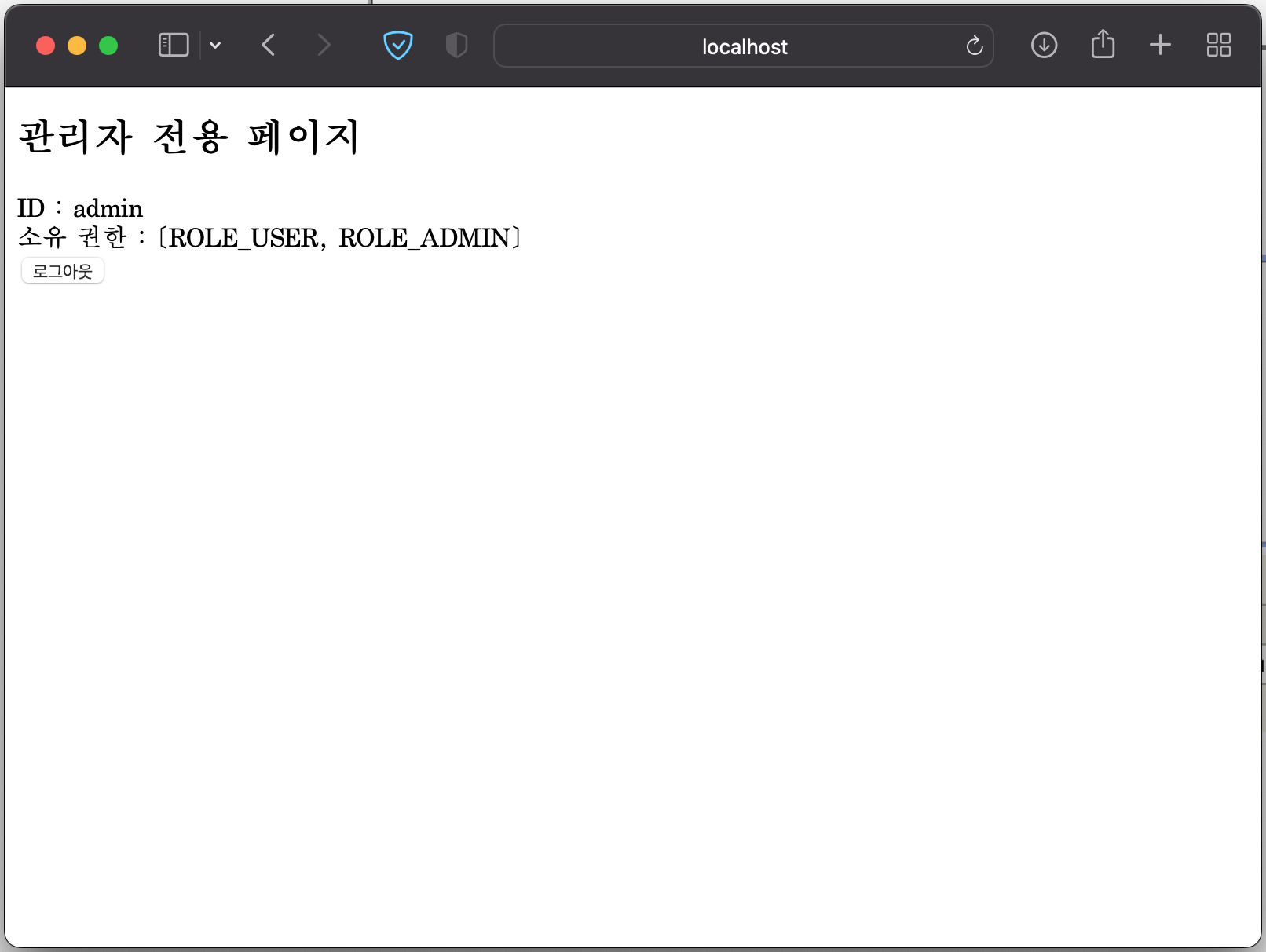
로그아웃하면 다시 로그인 화면으로 이동한다.
다음으로는 사용자로 가입을 하고 화면 접근을 확인해보자.
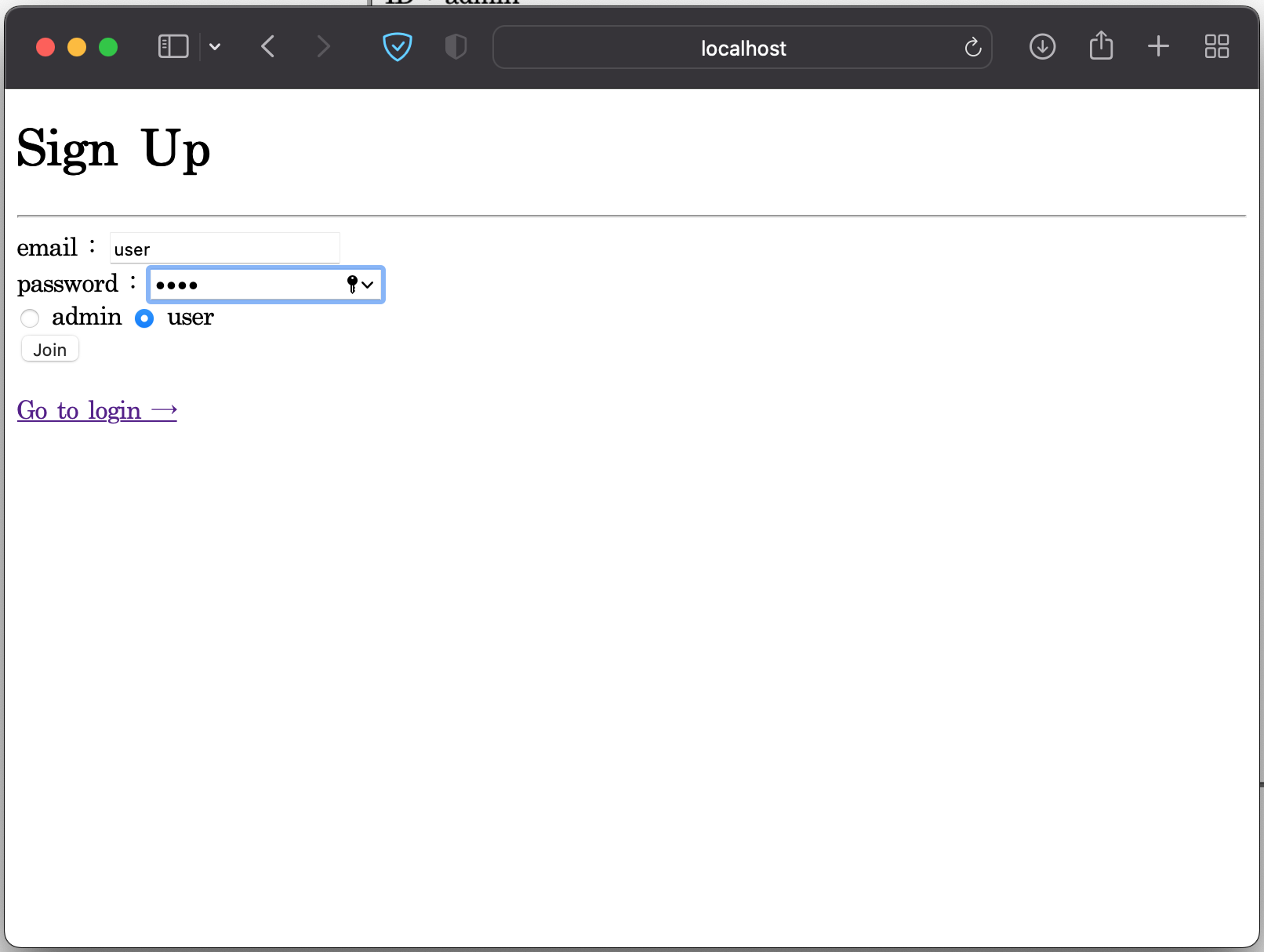


localhost:8080/admin 으로 접속 시도 시 위와 같이 403 오류가 발생하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
이것으로 실습을 마치자..
Reference : https://shinsunyoung.tistory.com/78
'개발이야기 > Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Boot JPA 게시판 - 글 등록/수정 (with MySQL) (0) | 2022.04.13 |
|---|---|
| Spring Boot JPA 게시판 - CRUD (with MySQL) (0) | 2022.04.11 |
| ORM (0) | 2022.04.03 |